
- Flash Memory
We use our computer hard disk to store all our files including documents, photos, PDF’s, MP3’s and so on. But, there are cases where you will need to store information in a much safer platform than your hard-disk. A device which can be carried around and can be easily interfaced with your PC for further operation. In such a case, the flash memory is the right solution. It is not only portable but also provides security than your hard-drive.
What is a Flash Memory?
Flash memory is a type of electrically erasable programmable read-only memory [EEPROM] chip that can be used for the transfer and permanent storage of digital data. It is actually a long-term persistent storage computer storage device that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed.
Working of Flash Memory
In this device, the information is stored as an array of floating gate transistors called cells. Each of these cells can store only one bit of information at a time. The design of each memory cell is somewhat similar to that of a MOSFET. The only difference is that this cell has two gates. The gate on top is called the control gate [CG], and the bottom one is called the floating gate [FG]. FG may be made of conductive materials like poly silicon or can also be non-conductive. These two gates are separated from each other by a thin oxide layer. To know the exact representation, take a look the figure given below.
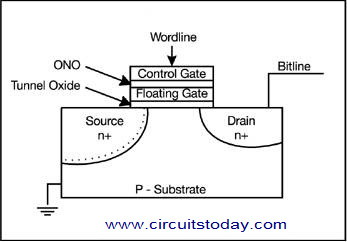
- Flash memory operation
The FG can come in contact with the word line only through CG. When that particular link is closed, the cell will have a value ‘1’. Inorder to change the value to ‘0’, a process called tunnelling has to be done. This charge cancels the electric field from CG, and thus causes to modify the threshold voltage [V] of the cell.
During the read process, a voltage that is below V is applied to CG. This V depends whether the channel should be conducting or insulating, which is in turn controlled by the FG charge. This causes the channel to know the current flow and hence the binary code is formed. This is the method of reproducing the stored data.
As told earlier, the flash memory can be read only with one byte at a time. But while erasing it, it must be erased as a block. In a block there are a lot of bytes. If you programme any of these bytes and later want to erase it, you will have to erase the whole block. So, in short, the device can offer you random access read and programming operations, it cannot offer you random access rewriting or erasing operations.
Advantages of Flash Memory
- Easy and fast transfer of data is possible
- The device is completely electronic rather than mechanical. So there are no moving parts in the device.
- This device is erased as well as re-programmed in large blocks. This mechanism is different from the typical EEPROM chip where erasing is doe in small blocks. So, it has an advantage of speed when writing large blocks of data into the device.
- As the device is extremely compact and packaged, it is completely water proof, pressure proof, and also has a high degree of durability.
- There are flash memories with a memory capacity of almost 16GB available.
Applications of Flash Memory
- Flash memory is the most widely used device in the field of home video game consoles. It has clearly replaced EEPROM chips and SRAM’s for saving data in video games.
- Flash memory is also used in personal digital assistants (PDA’s), digicams, mobile phones, laptops and so on.
- The device is used for firmware storage. In modern computers, the speed of the system is a very important factor. There is a speed difference between the memory bus of the computer and the parallel flash device. The access times of all the modern SRAM’s are below 10 nano seconds. This has urged companies to make shadow code stored in flash and into the RAM. This means that the code is first sent to the flash and then to the RAM for execution. This enables faster response from the CPU as well. Usually a serial flash drive is used for this purpose. As soon as the firmware is decided to be read, a compression is also added so that a smaller chip can be used. Some applications of serial flash include storing firmware for hard drives, DSL modems, wireless network devices, Ethernet controllers and so on.
Future of Flash Memory
1. As flash devices are completely electronic and not mechanical, it can be a great innovation if it can be used for a hard disk. It will surely be a good replacement as it is advantageous in the field of speed, access, power consumption and so on. But this technology is only being advancing and right now the cost factor is a huge perspective to be looked out for. The production of a flash based hard disk is higher than that of a normal one.
Another problem is regarding the support for the operating system. The finite number of erase/write cycles will make it unable to achieve.
2. Although the flash memory technology has been highly advanced, experts still believe that the device can replace all the major type of storage devices being used today.
Many companies have started using serial flash device for sequential data accessing. Since the device has lesser pins than the parallel flash memory it can be easily embedded onto a printed circuit board. Although it transmits and recieves only 1 bit at a time, the smaller size, lesser cost and low power consumption factors make this device more suitable. Since the number of pins are less, the size of the device is less, causing a reduction in area of the PCB. This also helps in PCB routing.

7 Comments
Hello
I want 8gb 16gb 32gb udp flash micro SD HC memory card PCB Design.
Plz tell me about it.
Thanks
Mohi Uddin Ahmed
Hello John what a nice blog that gives all information about flash memory such as its features , functions, advantages , its working etc. Thanks keep it up.
IT WONT HAVE MAGNETIC EFFECT AS OTHER STORING DEVICES HAVE.
YA ITS A RECENTLY BOOMING PRODUCT .
ITS A HOT TOPIC TOO.