The power of existing ledgers is limited because the data stored on them can be altered or deleted. Therefore they cannot be trusted to provide a clear transparent image. There exists a gap of trust in current business transactions. This is why we depend on third parties to maintain our finances and ensure that our ledgers reflect our true operations. We cannot do business without them.
What if we didn’t have to depend on third parties? What if we had some way to preserve the integrity of our ledgers on our own? That would eliminate the dependencies on all external intermediaries and empower individuals to manage their own affairs.
This is exactly what blockchain can do for us. Blockchains are distributed ledgers that are open to everyone. Everyone can look at them, but once data has been created not even the editor can tamper with them.
Blockchain functions like Wikipedia, anyone can alter the data in the blockchain and create new data. However, unlike Wikipedia, the data is not stored on a central server or regulated by a central party. Rather the data is stored in millions of computers worldwide and regulated by all the computers in the network. Once the data has been recorded inside the blockchain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter that data. In simpler words, a blockchain is a decentralized online ledger that records all transactions permanently without needing any authentication from any third party or intermediaries.
How does Blockchain Technology Work?
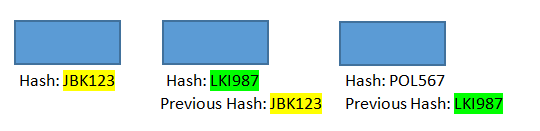
Blocks are the building blocks of the blockchain technology. Each block in the blockchain consists of three elements:
- Data
- Hash
- Previous Hash
Data
This is the information that has been stored inside the block. It varies from one blockchain to another. A blockchain containing the health record of the patient may record the temperature, blood pressure and heart rate of the patient at any particular time.
Hash
The Hash is the unique identification code of every blog. No two blocks in the blockchain can have the same hash code it is like the digital fingerprint of the blocks. If data inside the block is changed, the hash of the block changes as well thus creating a new block. This is what makes the blockchain so secure.
Previous Hash
Each block contains the hash of the previous block that it has evolved from. The common hash address between the newly created block and the original block is what creates the chain. It is this technology of digital stamping that makes the block chain so secure.
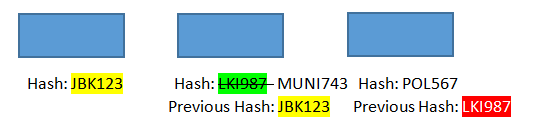
For instance, suppose there are three blocks A, B and C. The first block, called Genesis block, is unique because it is the first one in the chain, therefore, it will not have a hash address of the previous block.
The Blocks A, B and C are chained together due to the commonality in the hash address of two consecutive blocks. If someone tries to tamper block B and change the data stored on it, the hash address of block B will change.
This will make the chain invalid as the hash address of block B will no longer correspond to the hash address of Block C. Such a change can easily be detected in the system.
However, only hashing is not enough to keep the data secure. As modern computers are fast, hackers may override the whole chain by tampering with all the blocks in the chain and recalculating the hash codes. A mechanism called proof of work is used to add another layer of security to the blockchain. This mechanism slows down the creation of new blocks. In the case of bitcoins, it takes around 10 minutes to calculate the required proof of work and add a new block to the chain. This mechanism makes it extremely difficult to tamper with the blocks, because if you tamper with one block in the chain, you need to recalculate the proof of work of all the corresponding blocks in the chain.
Thus the blockchain provides a secure way to store data by making use of hashing and proof of work. Instead of using a centralized network, the blockchain stores data in decentralized a peer to peer network. Anyone and everyone is allowed to join this network. Anyone who joins the network gets a full copy of the blockchain on their computer. The node uses these copies to verify that everything in the blockchain is in consensus. When a new block is created, it is sent to all the computers in the network. Each node verifies the block to ensure that it has not been changed or tampered. Once the block has been verified, it is then added to the blockchain by all the nodes thus creating a consensus validating the block. Tampered blocks will be rejected by the computers on a network. To successfully change the data in a blockchain, the hacker will have to recalculate the hash codes of all the blocks in the chain, redo their proof of work, and take control of over 50% computers operating in the network. This makes it almost impossible to change the blockchain. Since the data is held publicly across all computers in the network, blockchain technology provides complete transparency and visibility into the data set. Since the data cannot be tampered, it can be trusted. This makes it possible to exchange sensitive documents such as ledgers, legal notices, and intellectual property without the need of intermediaries to maintain the integrity of the documents.
Blockchain systems are continuously evolving over time. They may have originally been introduced to support cryptocurrencies, but today more and more people are exploring other industries that can benefit from this groundbreaking technology. In the near future, it is quite possible that almost all business transactions will be carried out over blockchain. The role of banks and other intermediary institutions may be diminished as the World Wide Web becomes more accessible, more secure, and more transparent thus generating more trust to enable direct peer to peer business transactions.
History of BlockChain
The digital stamping technique behind blockchain was originally cited in a paper in 1991 that described that digital documents should be time stamped so that it is not possible to tamper them or backdate them. In 2008, this technology was mentioned again in a white paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” published by a person or group named Satoshi Nakamoto. The real identity of the Satoshi Nakamoto is unknown to this day. Bitcoins were officially launched in 2009.
The blockchain technology powering the bitcoins made it possible to have transparent transactions online with records of data and digital signatures that could neither be tampered nor be removed thus creating an environment of digital trust.
In 2009, for the first time in history, Bitcoin made it possible to send money all over the world without any intermediaries. This was a groundbreaking development because previously sending money online was a cumbersome, costly and lengthy process. Money could only be transferred through banks or other intermediary services which often charged a high fee for their services. With bitcoins, you can transfer your money anywhere in the world with just a few clicks.
May 2010 marked another milestone when Bitcoins were used in the first real-world transaction to buy a $3.9 pizza in exchange for 10,000 BTC. After that, the technology grew at an explosive rate and Bitcoins reached parity with the US dollar in February 2011. Bitcoins have seen many ups and downs along the way, but the technology has survived and it continues to gain more momentum day by day.
As 2014 set in, Investment started pouring into the blockchain technology as people realized that this technology has the potential to go far beyond just cryptocurrencies. Blockchain has the potential to disrupt all industries including but not limited to the financial firms, voting, healthcare industry, supply chain, transportation, contract management and more.
Inspired by the potential offered by blockchain technology, Buterin launched another cryptocurrency company Ethereum to compete with Bitcoin in the year 2015. The blockchain of Ethereum was more powerful than the blockchain of Bitcoin because it could not only record financial transactions, Ethereum could also record other assets such as loans or contracts. Ethereum also pioneered the use of “smart contracts”. Smart Contracts are self-executing contracts because the terms between buyers and sellers are written between the lines of code and distributed across the decentralized blockchain network. These contracts make it possible to conduct transparent and traceable business transactions online without any intermediaries. Many IT companies including Microsoft are intrigued by the potential of smart contracts in facilitating fast, transparent and cost-efficient business transactions. Smart contracts have the potential to radically transform the way businesses work today. Businesses can directly send legal documents to each other without having to spend a dime on authentication from any external intermediary service worldwide. Business Transactions take previously took days to process can now be conducted in mere minutes without compromising on the reliability of data in any way.
Today, Blockchain technology is considered as the groundbreaking technology that will empower web 3.0. A web that is shared, public and highly secure. One that provides an infrastructure that takes back the control from institutions and gives it back to the public. Just as smartphones had once transformed communication, blockchain will disrupt the business industry by eliminating the gap of trust in peer-to-peer transactions by maintaining an online, transparent, irreversible ledger. Blockchain goes far beyond just exchanging bitcoins and other cryptocurrencies. They’re the building blocks of a more robust form of the internet which empowers individuals and groups by inculcating a culture of trust and transparency.
Companies are now shifting from proof of work to proof of stake for validation of new blocks in the blockchain. Traditionally news blocks are added to the blockchain after they’ve been validated by a system known as proof of work. The proof of work is the process of validating the new block by using high computational power to solve complex mathematical problems. Proof of work is provided by miners who operate large data centres and exchange cryptocurrency for data security. Now the blockchain technology is shifting from proof of work to proof of stake. A system in which a person can validate the block based on his/her stake in the system. For instance, in a bitcoin blockchain a higher number of bitcoin owned by a miner will translate into a higher mining power. This makes the system more robust and faster than the system based on validation by proof of work. The first cryptocurrency to adopt proof of stake was Peercoin. Now more and more companies are moving from proof of work to proof of taking to save on computing power and time in validating the new blocks in the chains.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain is often used synonymously to cryptocurrencies mainly because it was first introduced as the mechanism behind bitcoins. However, Blockchain is much more than that. It is an encrypted decentralized database that maintains a record of all transactions distributed across potentially millions of computers worldwide. This means that once data has been recorded on the blockchain nobody can go back and change it.
Blockchain has the potential to instigate massive institutional and social change by curbing corruption and making the systems transparent and open to the public. Some say it may even drive the intermediary companies out of business.
Some of the major applications of blockchain outside of cryptocurrency are discussed below.
1. Preventing Voter Fraud
Digital Voter Fraud has been a hot topic since the US election in 2016. Whether there was Russian involvement in the US election or not, voter fraud is a problem that exists all over the world. Many countries still cast and count votes using traditional ballots because they fear data may be manipulated by hackers if it is stored online. However, manual counting of votes is not a reliable system either. Votes can easily tamper in a manual system. Manipulation of votes is a serious threat to democracy. This problem can be solved by using blockchain to record votes.
The blockchain has the potential to build a robust voting system that is a lot more transparent and secure than the systems that exist today.
The blockchain is ideal for a voting system because it can store each vote as a unique entity that can neither be erased nor corrupted after it has been created. The blockchain can process the votes with a lot more transparency as compared to the traditional balloting systems. Moreover, the high level of security inherent in the blockchain technology will prevent the hackers from manipulating the data before or after the elections. Another potential advantage of a voting blockchain is that it will increase the overall voter apathy. A digital voting system that allows the users to cast their votes from the comfort of their homes on their mobile phones or laptops is sure to encourage more people to participate in the voting process. The counting of votes will become a lot easier as well as all the data is recorded online.
Another benefit of moving the voting system to blockchain is the cost-effectiveness of the system. A single vote costs up to $25 in the current system. The cost can be reduced up to $0.50 per vote if a blockchain based voting system is implemented on a large scale.
2. Distributed Cloud Storage
The cloud storage that we have today is being controlled by centralized entities who have complete control over our data. This comprises the security of our data, and increases the dependencies on the service providers. The hacking incident of iCloud in 2014 shows us that there are loopholes in the data stored on cloud. Our personal data can easily be compromised if someone manages to crack the security of the cloud.
Blockchain can provide a good alternative to cloud storage by taking away the control from a centralized party and giving it back to the individuals. Distributed cloud storage works by shredding data files, securing them by encryption, and distributing them across the network. The only one who can access the files is the one who stored it.
This has the potential to give birth to a new model of storage in which the users can rent out the excess storage on their systems much like Airbnb. Storj has already started working on this model. They provide distributed cloud storage at extremely low costs. There are no charges for minimum usage or setup fees. While their system is a work in process, it has the potential to become the future of blockchain cloud storage.
With low costs, high speeds, and unbreakable security, distributed cloud storage will disrupt the cloud storage industry in the next few years.
3. Bank Access In Remote Areas
Many countries do not have a robust banking system in rural or remote areas. It becomes difficult to transfer money to these remote areas due to the lack of proper banking infrastructure. Branchless Mobile Banking has solved this problem to some extent, however, there is still a gap in the market for sending or receiving money from international accounts. Using services like Western union is quite costly, moreover, it takes a long time to process the transaction.
Cryptocurrencies make this exchange a lot simpler by processing the money transfers in less than an hour. Moreover, the process is much cheaper than using third-party services. People can now send money to their relatives in rural areas in almost all parts of the world with just a few clicks.
4. Supply Chain Tracking
Many organizations are using ERP systems in order to manage their supply chains efficiently. However these systems cannot provide proper transparency regarding the product.
Blockchain technology can be used to enhance the current supply chain tracking mechanisms.
Data regarding the product including its name, temperature, pressure and more could be documented each time the product changes hands moving from the manufacturer to the point of sale. As data stored on the blockchain cannot be altered, this will provide a transparent stream of data that can track the product as it moves from the manufacturer to the point of sale thereby reducing time delays and incurring cost efficiencies.
The database of record maintained on the blockchain will also validate all types of transaction thus facilitating the companies in passing internal and external audits of the system.
5. HealthCare
Blockchain can be used to enhance the functionality of the current electronic healthcare record systems. Currently, the electronic healthcare record systems being used in hospitals do not provide complete clarity and coherence in the data. It is not clear who added or edited the record and when. This lack of clarity makes it difficult for the decision makers to trust the data. Therefore same procedures and medical tests are conducted repeatedly to ensure that all the information is correct.
Moreover, another challenge that is being faced by the healthcare industry is the storage and sharing of medical data with all the stakeholders without compromising on the integrity and security of data.
The blockchain technology solves both of these problems. With blockchain, the complete medical record of a patient can be maintained in a single coherent chain of blocks. All entries that are uploaded on the blockchain are digitally stamped showing when the data was updated and who was responsible for it. This reduces the ambiguity in data and provides a clear image. Moreover, the integrity of the data can be protected by allowing restricted access to the data by using an authentication key. Each patient will have their own private authentication key. Data on the blockchain can only be accessed by providing the patient’s personal key.
Different sources of data can be used to update the blockchain. The patient’s data can be updated on the blockchain by using the doctor’s notes, or by uploading data from the patient’s wearable devices. This data is then encrypted and stored in the patient’s blockchain. If the data is to be retrieved, the patient’s private key is provided to gain access to the data. The data is decrypted and displayed on the screen.
This system of recording patient’s medical record gives the patients complete control over their medical data. Patients decide who can see their data and who cannot. Moreover, since everyone will have access to the same medical history of the patient, this reduces the risk of potential errors. Repetition of the data in the system is minimized.
This model of maintaining patient records is much more cost efficient than the current systems available in the market. It allows multiple users to make changes to the user’s data without compromising on the integrity of data. This allows easy access to patient’s information, simplifies billing and eliminates redundant administrative tasks.
Companies have already started implementing blockchain technology in the healthcare industry.
MedicalChain is a blockchain that is used for storing medical health records. It is used by medical practitioners and patients for viewing, recording and editing medical record. All record stored on the blockchain are auditable, secure and transparent and they’re recorded on the company’s distributed ledger. The patients have complete control over who can see their data, and how long can are they allowed to access it.
Blockchain technology offers limitless potential to enhance all our existing systems such as supply chains, Intellectual property rights, financial institutions, healthcare industry and more. By integrating blockchain with the internet of things and other technologies, we can explore a lot more.
Future of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is the future. It will become the basis on web 3.0 creating a more transparent web that eliminates the gap of trust that exists today. The revolution brought on by blockchain will not only be limited to financial institutions, it will disrupt all major industries.
They say that blockchain will do to banks what email did to communication. Cryptocurrencies have already started spreading across the world like wildfire. Banks and financial institutions are already researching how they can use this new form of capital to strengthen their business models. The virtual currency that can be shared across the world within minutes with people who didn’t have access to bank accounts before will open worlds of opportunity to people.
Governments having vested interests will not be able to hinder financial aid from reaching people by enforcing heavy taxation or regulations on banks. Blockchain will allow financial Aid to be sent to war-stricken countries like Syria in a matter of minutes. Moreover transferring money by using cryptocurrencies is much cheaper than transferring the same amount through banks due to the heavy service charges. Blockchain will make it much easier for us to help each other out without involving any third parties in the transaction.
The Internet of Things and Blockchain can join forces to become powerful tools that won’t be dependent on any centralized system. IBM and Samsung have already started working in this area under the umbrella of a project called ADEPT. Project ADEPT aims to empower IoT devices by using blockchain so they can directly communicate with each other to handle their updates, fix bugs, record performance and a lot more.
Blockchain may even eliminate the need for large data centres as distributed cloud storage becomes mainstream. People can save large amounts of data at extremely low costs in computers and devices all across the globe. There will be no need for centralized data storage anymore. No one will be able to access our data without our permission. This will eliminate many of the privacy concerns that cloud our minds today.
In the next two years, Dubai may move their government documents on the blockchain. This will lead to efficient operations based on transparent process. If Blockchain becomes mainstream in all governments, we can bid procrastination and red tape goodbye. The added transparency will reduce corruption, and speed up the proceedings.
Artists and musicians won’t have to depend upon large record companies to sell their music. They will be able to sell their music directly by conducting business using smart contracts. With all the legal paperwork out of the way, musicians will be able to sell directly to consumers without worrying about licensing issues.
The retail industry will no longer need PayPal and other such companies to validate the transactions. People will be able to do business online using smart contracts and receive payments in cryptocurrencies. Countries like Pakistan that do not have PayPal will not need to depend upon Western Union and other expensive alternatives. People can simply receive payments in bitcoins for all the services rendered. Instead of relying on third-party marketplaces like Amazon, this new world of retail powered by blockchain will have an inherent reputation management system that will gain trust based on past transactions recorded in the ledger. The companies will not need to borrow trust from big E-commerce names. They can build their own trust, and run their own business on their own rules without paying an extra dime to anyone else.
Real Estate deals will become from fraud and corruption. From verification of ownership to authentication of documents everything will become faster. Startups facilitating real estate records are already popping up. A system of real estate based on blockchain may be nearer than you think.
The next generation of the internet is already here, and it is evolving faster than ever before. The future is blockchain. Combined with Artificial intelligence and Internet of things, Blockchain will truly disrupt the reality that we know today. The outlook for the future seems a lot brighter than the past as it brings hopes of a brighter tomorrow for industries and individuals alike. The blockchain is not just bitcoin or a base for the cryptocurrency, It is the gateway to a whole new world.



Comments are closed.